Supporting materials
Instructions for students (Word document)
Instructions for students (PDF file)
Download
Download this article as a PDF

Contrary to the popular saying, deep waters are often far from still – which is just as well for marine life. Activities using simple water tanks are a good way to find out about the physics at work beneath the waves.

When we think about climate change, one of the biggest concerns is that major ocean currents such as the Gulf Stream are being sent off course, jeopardising the weather systems that depend on them. But what causes such currents to be established in the first place?
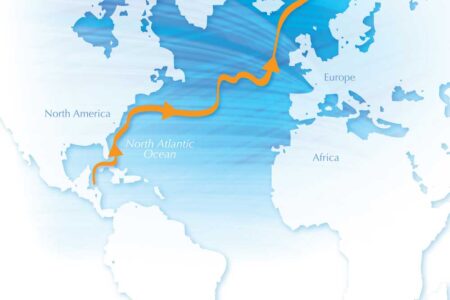
Part of the answer is gravity. Gravity acts on water masses of different density and this, together with wind and Earth’s rotation, produces forces and currents within the oceans. Such processes not only have a potential impact on our climate, but are also a huge influence on the environment inhabited by marine organisms.
As a result, any student of oceanography will need a good understanding of these processes. But a group of university oceanographers in Maine, USA, noticed a few years ago that their marine science students seemed unaware of the physics involved in their subject, focusing instead mainly on the biology. As a result, they decided to put together a teaching resource to convince students that oceans are an unusually exciting place to study physics. This article is based on that resource (Karp-Boss et al., 2009), which focuses on key concepts in physics that are also fundamental in oceanography, and provides a compelling environmental context for ideas within physics.
Of course, students learn best when they are actively engaged, so central to the resource is a series of activities designed to engage students and challenge their assumptions. Two activities that the oceanographers have used successfully in their classes are described here: one focusing on density, the other on waves. Both could be used with secondary-school students of all ages (11-19).
The first activity shows how stratification occurs as a result of density differences due to temperature or salinity. The second activity looks at internal waves; resonance and natural frequency are also demonstrated. For both activities, the apparatus is set up prior to class, and the students carry out the activities for up to 30 minutes per activity (using worksheets, below and available for download from the Science in School websitew1). The last part of the lesson is used for summarising findings and discussion.
Density is a fundamental property of matter. It is the mass per unit volume of a material – that is, how much mass is packed into a given volume. In oceanography, density is used to characterise water masses and to study ocean circulation. Many ocean processes are caused by differences in densities: large-scale ocean circulation and carbon transport by particles sinking from surface to deep waters are just two examples.
Whereas the density of water ranges from 998 kg/m3 for fresh water at room temperature to nearly 1250 kg/m3 in salt lakes, ocean waters have a much smaller density range (about 1020–1030 kg/m3). Most of the variability in seawater density is due to salinity and temperature. As salt concentration increases, due to evaporation or ice formation, density increases. Higher temperatures reduce density, whereas cooling increases it.
Ocean seawater density increases with depth, but not in a uniform way: instead, water of different densities forms a series of layers (figure 1).
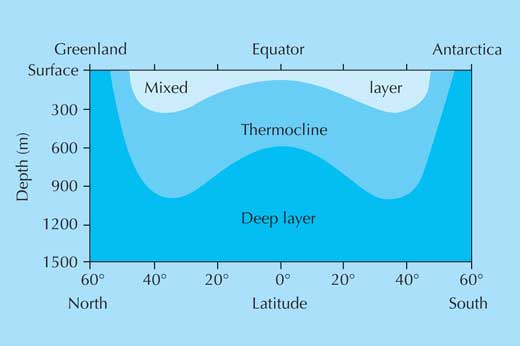
This stratification acts as a barrier for the exchange of nutrients and dissolved gases between the top, sunlit layer where phytoplankton thrive, and the deep, nutrient-rich waters. Mixing stratified layers requires work: think how hard you need to shake a bottle of salad dressing to mix the oil and vinegar. So, without enough energetic mixing due to wind or breaking waves, phytoplankton at the ocean’s surface will lack nutrients.
 Plankton
Plankton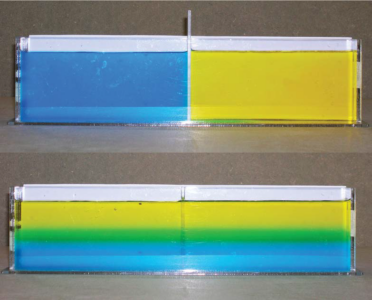 Density layers. The top image shows the tap water and salt solution before the divider is removed. Afterwards (lower image), the salt solution forms a stable layer at the bottom of the tank with the tap water above it.
Density layers. The top image shows the tap water and salt solution before the divider is removed. Afterwards (lower image), the salt solution forms a stable layer at the bottom of the tank with the tap water above it.
Image courtesy of Lee Karp-Boss
 Density is fundamental to how lakes freeze. As winter approaches in high latitudes, lake waters are cooled from the top. When the upper waters become cooler and denser than the waters below, they sink. The warmer, less dense water underneath then rises to replace the sinking water. If low air temperatures persist, these processes will eventually cool the entire lake to 4 °C – the temperature of maximum density for fresh water. With yet further surface cooling, the density of the upper waters will decrease, and the lake becomes stably stratified with colder but less dense water at the top. As surface waters cool to 0 °C, they begin to freeze. If cooling continues, the frozen layer deepens.
Density is fundamental to how lakes freeze. As winter approaches in high latitudes, lake waters are cooled from the top. When the upper waters become cooler and denser than the waters below, they sink. The warmer, less dense water underneath then rises to replace the sinking water. If low air temperatures persist, these processes will eventually cool the entire lake to 4 °C – the temperature of maximum density for fresh water. With yet further surface cooling, the density of the upper waters will decrease, and the lake becomes stably stratified with colder but less dense water at the top. As surface waters cool to 0 °C, they begin to freeze. If cooling continues, the frozen layer deepens.
Although density is not the first thing that comes to mind when we think of the sea, waves are a different matter. Waves are ubiquitous in the ocean, in lakes, and of course on beaches – and they are feared in their destructive form as tsunamis.
Most of these waves are what physicists call surface waves. But there are also internal waves, which occur at the interface between density layers of water. In the ocean, breaking internal waves mix up the water layers and lift the nutrients they contain.
The geometry of a water basin (such as a lake or a bay) determines which waves are excited when force is applied and then released (e.g. due to a passing storm). These waves are the ‘natural modes’ of the basin – in a similar way to sound waves in a musical instrument, where a particular frequency is produced by a given length of string or air column. This phenomenon is called resonance.
In oceanography, there is an additional phenomenon known as seiche (pronounced ‘saysh’, from an old French word meaning ‘to sway’). This is when a standing wave is established in a semi-enclosed body of water, which moves from side to side as a mass – rather like tides. For example, the Adriatic seiche, which has a period of 21.5 hours, is associated with serious floods in Venice, Italy. Other naturally occurring examples of seiches have been observed in Lake Geneva and in the Baltic Sea.

The energy of internal waves is generally lower than that of surface waves. This is because the gravitational restoring force is smaller for internal waves, due to the relatively slight difference in density between water layers (compared to that between water and air for surface waves). This lower energy means that, for a tank (or water basin) of a given size, the natural frequency of the internal waves will also be lower than for surface waves.
In additional to surface waves, stratified fluids support internal waves; in two-layer fluids, these waves ride on top of the interface between the two fluids. Their periods are significantly longer than those of surface waves and their amplitudes can be significantly higher. When we perturb the two-layer system, many waves are initially excited, but only those that fit (resonate) with the geometry of the basin remain. Inserting the piece of plastic at one end of the tank, simulating an increasingly shallow seabed, can cause internal waves to break, similar to surface waves breaking on a beach, but occurring below the surface.
This article is based on the resource developed through the organisation COSEE (Center for Ocean Sciences Education Excellence) by oceanographers Lee Karp-Boss, Emmanuel Boss, Herman Weller, James Loftin and Jennifer Albright (Karp-Boss et al., 2009).
Physics is often seen as unrelated to everyday life, which makes many students uninterested in the subject. This article uses oceanography to provide a context for physical concepts, thus helping to raise students’ interest. It could be used in biology or physics lessons, particularly when studying marine topics.
The two activities described can either be used by teachers as demonstrations or carried out by students. They can be used before explaining the physics concepts that appear in them (to make students think about them) or after their explanation. Additional exercises about physical oceanography that would be useful for teaching physics to students aged 12-18 are listed at the end of the article.
Finally, the text could help students understand that seemingly diverse scientific subjects can be interlinked. For example, to understand how the environment affects marine life, we need concepts from physics (and also chemistry and geology).
Mireia Güell Serra, Spain
Instructions for students (Word document)
Instructions for students (PDF file)
Download this article as a PDF